A staggering 73% of small business owners and leaders experienced data breaches or cyberattacks in the past year. This surge in incidents is present because SMEs are frequently targeted by cybercriminals who assume these businesses have weaker defenses compared to larger organizations. This can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions, making robust cybersecurity measures essential for their survival and growth.
Understanding Cybersecurity Threats
Businesses face various security threats that can can have severe consequences if not properly addressed. Some of the most common threats in 2023 are:
Phishing
Phishing is the most common cyber threat that’s disrupted organizational workflow for many companies – small, medium, and large. It’s a type of social engineering attack where the hacker gains unauthorized access to confidential information, like login details or bank account information. They might trick users into revealing this data by sending a malicious link over communications channels, like email or SMS.
The moment you click on it, you are redirected to a malicious website that will get quick access to your private data. Educating employees about these attacks and implementing robust authentication tools can mitigate the risk of phishing to some degree, but it’s best to hire a specialized cybersecurity team to manage the risk of such attacks.
Malware
Malware is malicious software, which gives hackers easy access to a company’s private network or system. They can view and control the resources remotely without your knowledge.
In most cases, businesses remain unaware of the malicious codes running on their system until a serious loss or damage to the organization occurs. Keeping your security software and network up-to-date with the latest technology can mitigate the risks of these attacks, but for comprehensive protection, a firewall is a must.
Insider Threats
Verizon’s data Breach Investigation report shows that 25% of attacks are from insider threats. No one has as much access to your business’s confidential data as your employees. Dissatisfied employees or greedy ones might plan a cyber-attack on your organization by leaking the data to third parties or those who can misuse it to destroy the company’s reputation.
Remote Network Vulnerabilities
It’s been continuously advised to not use public Wi-Fi or connect to an unsecured network at random places. Attackers can use the network’s vulnerabilities to their advantage and may gain access to your system. Even the network at home is vulnerable to attacks because of the lack of security and technical expertise. Working with a dedicated security provider who can remotely manage your systems seems the most reliable way to prevent these attacks.
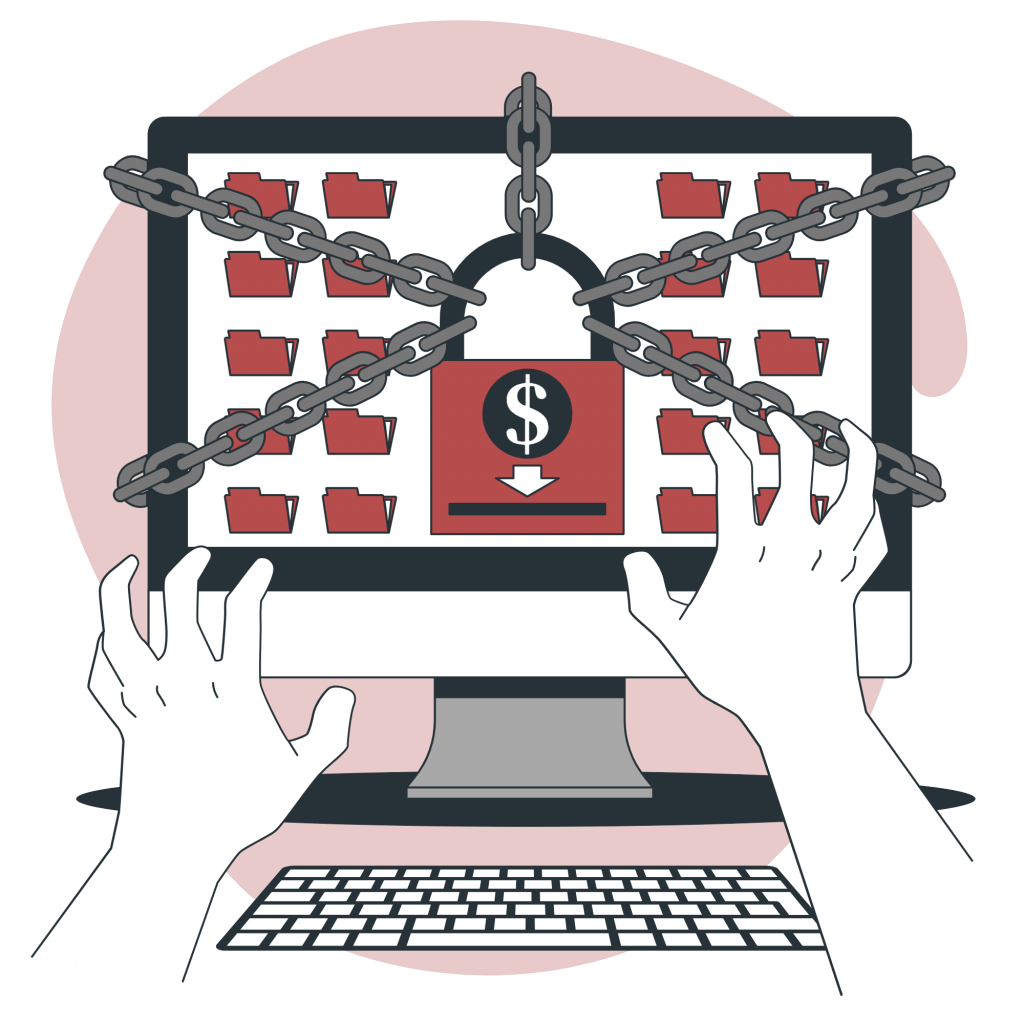
Ransomware
The ransomware attacks were on the rise in 2020. With a majority of land-based businesses closing and eCommerce sales becoming a new norm, attackers got a golden opportunity to conduct ransomware attacks. We saw a massive spike (148%) in ransomware attacks during the pandemic. It continued in 2021. Now, it’s expected to be one of the biggest cyber threats in 2023.
An attacker can deploy malware into your system, which restricts your access to the company’s sensitive data. You need to pay a ransom to retrieve the locked-up data or the attacker threatens to leak it to the public. The worst part is that there’s no guarantee the hacker will give you access to your database back after receiving the ransom.
Essential Cybersecurity Measures
It’s crucial for any business to implement adequate security measures to protect their digital assets and keep their operations running smoothly.
Strong Password Policies
Use strong, unique passwords, supported by password managers and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Regular Software Updates
Enable automatic updates and conduct regular checks to patch vulnerabilities.
Employee Training and Awareness
Educate employees on recognizing threats like phishing and safe internet practices through labs and regular training sessions.
Data Backup Solutions
Implement automated backups with offsite storage and regular testing to ensure data recovery in case of an incident.
Implementing Security Solutions
Businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture by adopting a range of affordable solutions that provide robust protection without hurting the budgets.
Firewall and Antivirus Protection: Firewalls act as a barrier between your internal network and external threats, while antivirus software detects and removes malicious software from your endpoints. There is a wide range of options for both firewall and antivirus solutions, allowing businesses to implement what suits them best. We offer solutions for both network and endpoint protections, which can be customized for each customer’s needs.
Use of VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): VPNs secure your internet connection by encrypting data in transit, making it difficult for attackers to intercept and steal sensitive information. This is particularly important for remote work, which is becoming more and more common today. Our VPN solution allows for secure end-to-end communication and easy management.
Secure Cloud Services: Cloud services provide scalable data storage and collaboration tools, reducing the need for expensive on-site infrastructure. Configuring adequate access controls and advanced detection & response is a key part of business continuity and growth. Our approach to securing the cloud takes into consideration each customer’s specific risks and reduces the attack surface by employing XDR, Vulnerability scanning and proactive Threat intelligence.
Incident Response & Recovery
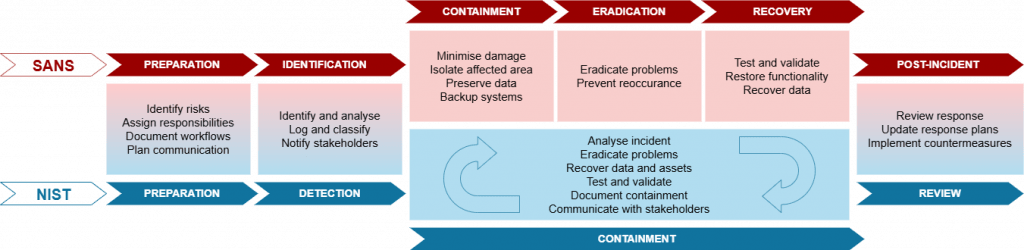
An effective incident response and recovery plan is critical for organizations to minimize damage and restore normal operations quickly following an incident. Here’s a detailed look at the essential steps involved:
The foundation of a strong incident response plan is Preparation. This involves defining roles and responsibilities, establishing communication channels, and creating a detailed plan of action. Regular training and drills ensure that all employees know what to do in the event of an incident. Preparation also includes having up-to-date contact information for key personnel and external partners, such as cybersecurity experts and legal advisors.
The first step in responding to an incident is Identifying that it has occurred. This requires continuous monitoring of your systems for unusual activity or signs of a breach. Effective identification involves using tools such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, and antivirus software. Employees should also be trained to recognize and report suspicious activity.
Once an incident is identified, the immediate priority is to contain it to prevent further damage. Containment strategies can be divided into short-term and long-term actions. Short-term containment might involve isolating affected systems, disconnecting them from the network, or disabling certain functionalities. Long-term containment includes more permanent measures, such as applying patches, changing passwords, and enhancing security configurations to prevent recurrence.
After containing the incident, it’s crucial to identify and Eliminate the root cause. This may involve deleting malware, closing vulnerabilities, and taking steps to ensure that the same type of attack cannot happen again. A thorough investigation should be conducted to understand how the breach occurred and what systems or data were affected. Eradication might also include forensic analysis to uncover any hidden threats and ensure complete removal of malicious code.
The Recovery phase involves restoring and validating system functionality. This includes bringing affected systems back online, restoring data from backups, and ensuring that systems are secure before resuming normal operations. During recovery, it’s important to monitor everything closely for any signs of lingering issues or further attacks. Testing and validation are crucial to confirm that all vulnerabilities have been addressed and that systems are operating as expected.
After an incident has been resolved, it’s essential to conduct a post-incident review to identify Lessons Learned. This involves analyzing what happened, how it was handled, and what could be improved. The findings from this review should be used to update the incident response plan, enhance security measures, and train employees. Sharing lessons learned with the entire organization can help prevent future incidents and improve overall cybersecurity posture.
This proactive approach not only protects the business but also builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity. For organizations looking to enhance their security posture without the heavy lifting, our services provide expert guidance and affordable solutions tailored to your unique needs, ensuring your business remains resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Conclusion
In today’s digital world, cybersecurity is vital for businesses of all kinds. By implementing basic measures and affordable solutions, such as strong passwords, regular updates, and incident response plans, businesses can protect themselves from common threats like phishing and malware. Prioritizing cybersecurity ensures ongoing operations and builds resilience against evolving risks, ensuring the future success of your business.